
By Mehdi Benatiya Andaloussi, Nina Biljanovska, Alessia De Stefani, and Rui Mano
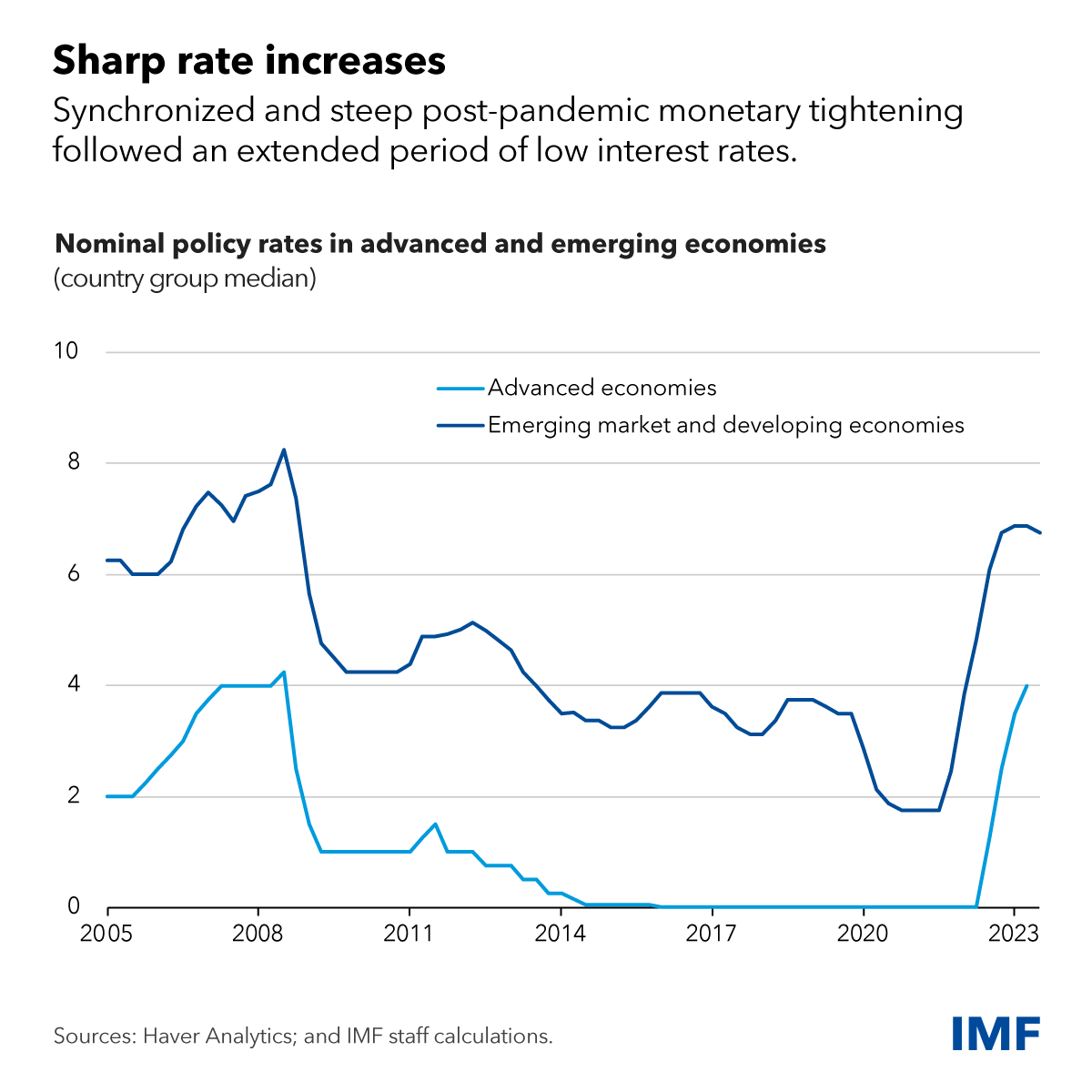
Central banks have raised interest rates significantly over the past two years to combat post-pandemic inflation. Many thought this would lead to a slowdown in economic activity. Yet, global growth has held broadly steady, with deceleration only materializing in some countries.
Why are some feeling the pinch from higher rates and not others? The answer partly lies in differences in mortgage and housing market characteristics. The effects of rising monetary policy rates on activity partly depend on housing and mortgage market characteristics, which vary significantly across countries, as we show in a chapter of our latest World Economic Outlook.
Housing is an important channel of monetary policy transmission. Mortgages are the largest liability for households, with housing often serving as their only significant form of wealth. Real estate also accounts for a large share of consumption, investment, employment, and consumer prices in most economies.
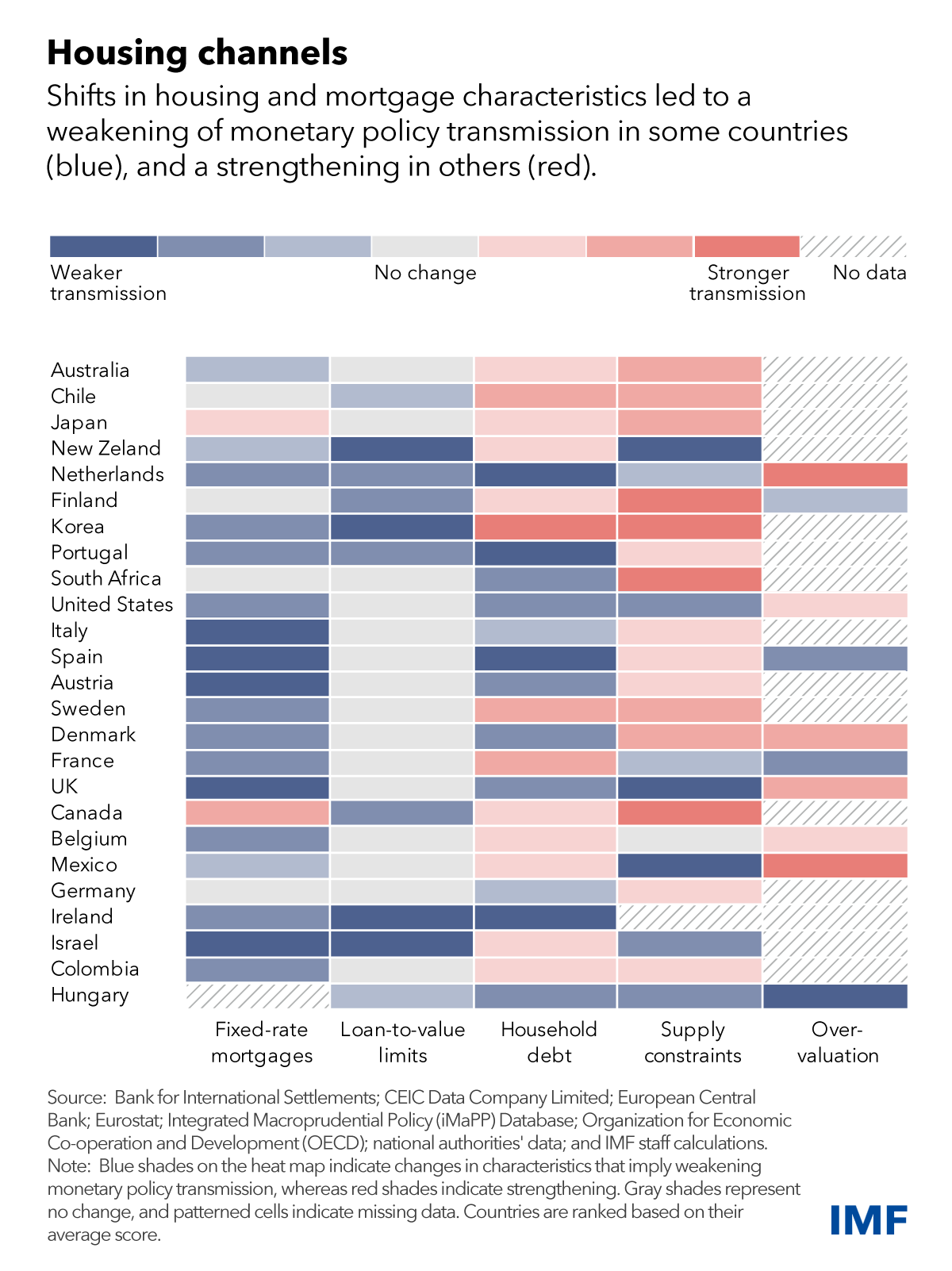
To assess how key housing characteristics impact the effects of monetary policy on activity, our research leverages new data on housing and mortgage markets compiled across countries: we find that those characteristics vary significantly across countries. For example, the share of fixed-rate mortgages in all country-level mortgages can vary from close to zero in South Africa to more than 95 percent in Mexico or the United States.

Our results indicate that monetary policy has greater effects on activity in countries where the share of fixed-rate mortgages is low. This is due to homeowners seeing their monthly payments rise with monetary policy rates if their mortgage rates adjust. By contrast, households with fixed-rate mortgages will not see any immediate difference in their monthly payments when policy rates change.
The effects of monetary policy are also stronger in countries where mortgages are larger compared to home values, and in countries where household debt is high as a share of GDP. In such settings, more households will be exposed to changes in mortgage rates, and the effects will be stronger if their debt is higher relative to their assets.
Housing market characteristics also matter: the transmission of monetary policy is stronger where housing supply is more restricted. For example, lower rates will decrease borrowing costs for first-time home buyers and increase demand. Where supply is restricted, this will lead to home price appreciation. Existing owners will see their wealth increase as a result, leading them to consume more, including if they can use their home as collateral to borrow more.
The same holds true where home prices have recently been overvalued. Sharp price increases are often driven by overly optimistic views about future house prices. These are typically accompanied by excessive leverage, prompting spirals of falling home prices and foreclosures when monetary policy tightens, which can lead to starker income and consumption declines.
Weaker housing transmission
Mortgage and real estate markets have undergone several shifts since the global financial crisis and the pandemic. At the beginning of the recent hiking cycle and after a long period of low interest rates, mortgage interest payments were historically low, the average maturity was long, and the average share of fixed-rate mortgages was high in many countries. In addition, the pandemic led to population shifts away from city centers and to relatively less-supply-constrained areas.
As a result, the housing channels of monetary policy may have weakened, or at least been delayed, in several countries.
Country experiences vary widely. Changes in mortgage market characteristics in countries such as Canada and Japan suggest a strengthening of the transmission of monetary policy through housing. This is driven mainly by a declining share of fixed-rate mortgages, an increase in debt, and more constrained housing supply. By contrast, transmission seems to have weakened in countries such as Hungary, Ireland, Portugal, and the United States, where characteristics have moved in the opposite direction.
Calibrating policy
Our findings suggest that a deep, country-specific understanding of housing channels is important to help calibrate and adjust monetary policy. In countries where the housing channels are strong, monitoring housing market developments and changes in household debt service can help identify early signs of overtightening. Where monetary policy transmission is weak, more forceful early action can be taken when signs of overheating and inflationary pressures first emerge.
What about now? Most central banks have made significant progress toward their inflation target. It could follow from the discussion that, if transmission is weak, erring on the side of too much tightening is always less costly. However, overtightening, or leaving rates higher for longer, could nevertheless be a greater risk now.
While fixed-rate mortgages have indeed become more common in many countries, fixation periods are often short. Over time, and as rates on these mortgages reset, monetary policy transmission could suddenly become more effective and so depress consumption, especially where households are heavily indebted.
The longer time rates are kept high, the greater the likelihood that households will feel the pinch, even where they have so far been relatively sheltered.
Mehdi Benatiya Andaloussi is an economist in the World Economic Outlook Division of the IMF’s Research Department. Nina Biljanovska and Alessia De Stefani are IMF economists. Rui C. Mano is a deputy division chief in the IMF’s Research Department. This article was originally posted here.
9 Comments
It will then come as no surprise that artificially high house prices also mean artificially high mortgages.
This is a double negative in that house prices could more easily fall resulting in lost equity, and the debt remains on which you could also be subject to interest rate rises.
Sounds familiar to many right now, and more to come.
House prices haven't plunged so far, at least not where I live, despite predictions here of an enormous crash. In fact in the year to Feb, Auckland house prices increased 3.72%.
The last year or two have been the perfect time to sniff out a bargain.
We want a better system that doesn't rely on one person loosing for another to make money.
Time will tell if it was a bargain rather than any present good management.
There has been a system like that in past...it was called communism. It still exists in North Korea.
Might want to tuck your greedy boomer in - it's showing again.......
North Korea is all about a lot of people loosing while a few making a killing, both figuratively and literally.
But ironically, one of the most free enterprise places on earth, Texas, has housing policies that make it uneconomic for extractive speculative rentier types like yourself to operate.
Developers there make their money by offering real amenity benefits.
Dp
The Crash in House prices NZ wide, while welcome, is hated by the selfish vested types, yet will continue until they more closely match earnings.
Auckland is already back in REAL Terms by -40% and Wellington is back -48%, over the last 3 years.
The Biggest crash in 45 years.
Housing has been the worst value store in NZ, in recent memory. Over the last 3 years our money has deflated 20%- while housing tanked in Nominal Terms
Some people in NZ cannot read statistics its seems, or just love having heads deep in the sand......
But it hasn't crashed, sure it's come back, Auckland prices are up 3.72% in the year to Feb. My neighbour just sold for $300k over CV...what crash? A lot depends on the area.
The last couple of years have been the perfect time to dip your toes in the property water.
Go for drive up SH16, it's chaos, and this is just the beginning. There's about 10 major projects planned for that area, some are already underway like the huge retirement village in Huapai and the widening of SH16.
Lots of money's going to be made out there. Who wants to get rich(er). Not many here I think. Reputedly NZ's biggest landowner has just completed 2 subdivisions north of Auckland, and they're on the market.
When I undertake projects like renovations, or a new build, I employ quite a few people, a bad thing apparently according to the socialists here. Property projects involve large sums of money, there's lots of risk, and that's not for everyone I guess.

We welcome your comments below. If you are not already registered, please register to comment
Remember we welcome robust, respectful and insightful debate. We don't welcome abusive or defamatory comments and will de-register those repeatedly making such comments. Our current comment policy is here.